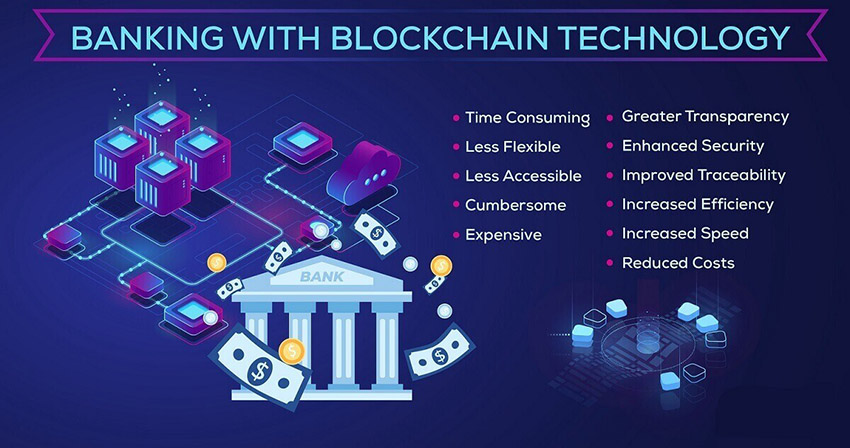
Blockchain technology, originally introduced as the underlying system for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has rapidly evolved into a transformative tool with vast potential to revolutionize industries, particularly in the financial sector. Blockchain is essentially a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, making it transparent, secure, and efficient. Its potential to improve the efficiency and security of financial transactions is significant, with many financial institutions and fintech companies exploring its possibilities.
In this article, we will explore how blockchain can enhance the financial industry’s operations, reduce risks, and improve transaction efficiency, while also addressing some of the challenges and limitations associated with its adoption.
1. Understanding Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that stores information across a decentralized network of computers, known as nodes. Each transaction or piece of data is recorded in a “block,” which is then linked or “chained” to previous blocks, forming a secure, immutable record of all transactions.
1.1 Key Features of Blockchain
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems, where a central authority oversees transactions, blockchain is decentralized. This means there is no single point of control, and every participant in the network has access to the entire ledger, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Transparency: Since every transaction is recorded on a public ledger that is visible to all participants, blockchain offers unparalleled transparency. This transparency is particularly useful in financial transactions, where it enables all parties to verify the integrity of the data.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This ensures that the transaction history remains tamper-proof and secure, making it nearly impossible to manipulate data.
- Security: Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure transactions, making it highly resistant to fraud, hacking, and unauthorized tampering.
2. How Blockchain Enhances Efficiency in Financial Transactions
Blockchain has the potential to streamline financial transactions in various ways, improving the efficiency of processes across the financial ecosystem.
2.1 Faster Transactions
Traditional financial systems, such as banks and payment processors, often involve intermediaries that slow down transactions. For example, cross-border transactions can take several days to process due to the involvement of multiple banks and clearinghouses. Blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries, enabling peer-to-peer transactions that can occur in real time or within a few minutes.
- Example: With blockchain technology, international money transfers can be completed in seconds, reducing the processing time from days to minutes. This is especially beneficial for businesses and individuals who need to send money across borders quickly and cost-effectively.
2.2 Lower Transaction Costs
The use of intermediaries in traditional financial systems adds costs to transactions, including fees for processing, clearing, and settlement. Blockchain technology allows for peer-to-peer transactions, cutting out the middlemen and thus lowering transaction costs. This can make financial services more affordable, particularly for smaller businesses and individuals who might otherwise be burdened by high fees.
- Example: Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies often have lower transaction fees compared to traditional banking services and remittance providers, allowing for more efficient and affordable financial transactions, particularly in cross-border payments.
2.3 Improved Efficiency in Settlements and Clearings
In traditional financial systems, the process of settling and clearing financial transactions can take several days. Blockchain speeds up this process by providing a real-time settlement of transactions, which is especially valuable in securities and derivatives trading.
- Example: In the case of stock trading, clearing and settlement can take up to two days (T+2) in traditional markets. Blockchain’s real-time settlement capability allows for near-instantaneous trade settlements, reducing settlement times and improving the liquidity of markets.
2.4 Automation with Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions encoded directly into the blockchain. They automatically execute transactions or actions when certain conditions are met. In the financial industry, smart contracts can automate processes such as loan agreements, insurance payouts, and asset transfers, reducing the need for manual intervention and the risk of human error.
- Example: In a loan agreement, a smart contract can automatically release funds to the borrower once the loan conditions are met, such as the borrower providing collateral or reaching an agreed-upon repayment milestone. This reduces delays, administrative costs, and potential disputes.
3. How Blockchain Enhances Security in Financial Transactions
One of the most compelling features of blockchain technology is its ability to enhance security in financial transactions. By utilizing advanced cryptography and decentralized consensus mechanisms, blockchain offers several key benefits in securing financial systems.
3.1 Enhanced Data Integrity
Blockchain’s immutability ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or tampered with. This is particularly important in the financial sector, where the integrity of transaction data is crucial. Every block in the blockchain is linked to the previous block, and changing any information in one block would require altering every subsequent block, which is computationally impractical.
- Example: If a financial institution records a transaction on a blockchain, it can be assured that the transaction history cannot be changed. This provides an added layer of security against fraud and data manipulation, which are common risks in centralized financial systems.
3.2 Prevention of Fraud and Cyberattacks
Traditional financial systems are vulnerable to cyberattacks and fraud due to centralized control and the reliance on single points of failure. Blockchain’s decentralized nature significantly reduces the risk of these types of attacks. Since blockchain data is distributed across multiple nodes, it is more difficult for hackers to gain access to the entire network or alter transaction records.
- Example: A hacker attempting to manipulate a financial transaction on a blockchain would need to gain control of more than 50% of the network’s nodes, which is virtually impossible in a well-distributed system. This makes blockchain a highly secure platform for financial transactions, reducing the risk of cyberattacks and fraud.
3.3 Cryptographic Security
Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure transactions, ensuring that only authorized parties can access and approve transactions. Public and private keys are used to verify the identities of participants, and digital signatures confirm the authenticity of transactions. This prevents unauthorized access and ensures the confidentiality and integrity of the transaction data.
- Example: In a cryptocurrency transaction, a user’s private key is used to sign and authorize the transaction. Only the owner of the private key can initiate the transaction, making it nearly impossible for someone to steal or alter the funds without the proper key.
3.4 Increased Transparency and Auditability
Because every transaction is recorded on the blockchain and is visible to all participants in the network, there is an inherent level of transparency that enhances security. Financial institutions and regulators can audit transactions in real time, ensuring compliance with regulations and reducing the likelihood of fraudulent activities.
- Example: Regulators can use blockchain technology to trace the flow of funds and verify that financial transactions are legitimate, improving transparency and reducing the risk of money laundering or other illicit activities.
4. Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain in Financial Transactions
Despite the many advantages of blockchain, there are several challenges and limitations that must be addressed before it can be widely adopted in the financial sector.
4.1 Scalability Issues
One of the main challenges facing blockchain is scalability. As more users and transactions join the network, the blockchain can become slower and less efficient. For example, Bitcoin can only process around 7 transactions per second, while traditional financial systems like Visa can handle tens of thousands per second. Scaling blockchain technology to handle high volumes of transactions is a significant challenge that developers are actively working to address.
4.2 Regulatory and Legal Concerns
The regulatory environment surrounding blockchain and cryptocurrencies is still evolving. Governments and financial regulators are working to establish guidelines and frameworks to ensure that blockchain technology complies with existing financial regulations, such as anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements. The lack of clear regulatory guidelines can hinder the widespread adoption of blockchain in the financial industry.
4.3 Energy Consumption
Some blockchain networks, particularly those that use proof-of-work consensus mechanisms (such as Bitcoin), consume significant amounts of energy. The environmental impact of blockchain’s energy usage is a concern, and more energy-efficient alternatives like proof-of-stake are being developed.
4.4 Integration with Legacy Systems
Many financial institutions still rely on legacy systems that are not compatible with blockchain technology. Integrating blockchain with these existing systems can be complex and costly, and it may take time for institutions to fully adopt blockchain in their operations.
Conclusion
Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize the financial sector by improving the efficiency, transparency, and security of financial transactions. By enabling faster, cheaper, and more secure transactions, blockchain can reduce operational costs, eliminate intermediaries, and enhance the overall customer experience. Moreover, its cryptographic security and immutability make it an ideal solution for combating fraud, reducing cyberattacks, and ensuring the integrity of financial data.
However, there are still challenges to overcome, such as scalability, regulatory concerns, and integration with existing systems. Despite these hurdles, the benefits of blockchain technology are clear, and its impact on the financial industry will likely continue to grow in the coming years. Financial institutions, fintech companies, and regulators must collaborate to address these challenges and unlock the full potential of blockchain in transforming financial transactions.